Brute-force Starter Test
If the engine won't crank when you turn the key, first be sure
one of the interlocks isn't engaged. For tractors with a clutch,
the clutch must be fully depressed. The PTO needs to be
disengaged. Tractors with hydrostatic transmissions must be in
neutral.
Once you have verified that you haven't created the problem by (for
example) having the PTO engaged, you want to determine if the problem
is associated with the battery, battery cables, and starter or with the
contol signal that energizes the starter.
Brute-force Starter Test. Refer to this starter diagram:
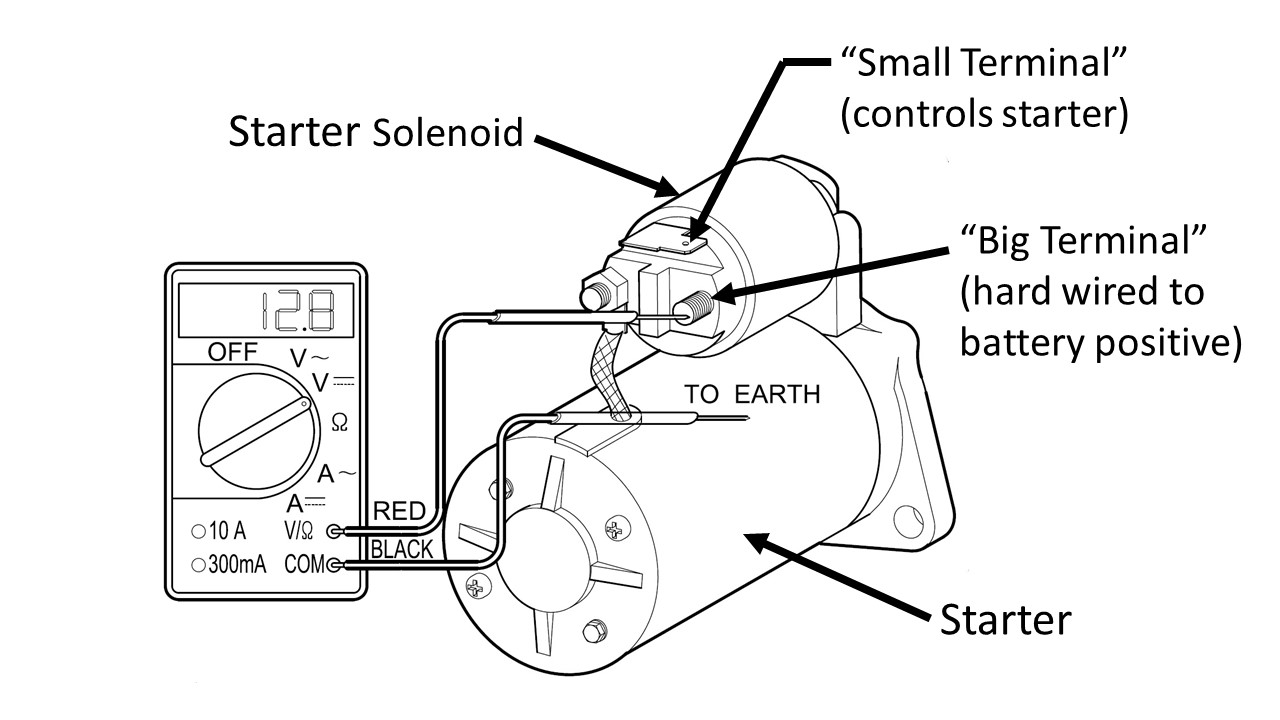
On Kioti tractors, the starter is located low on the left side
near the back of the engine. The starter case is connected to
battery negative through the engine block. The battery positive
cable is connected directly to the "big" outside terminal of the
solenoid. The other large terminal feeds power to the
starter when the solenoid is energized. In addition, there is a small spade terminal on the
top of the solenoid. When this small terminal is energized with +12v, the
solenoid closes a heavy-duty contactor that provides battery
power to the starter motor while simultaneously forcing the starter motor's pinion gear
to engage the flywheel gear.
If you measure the voltage (to chassis ground) at the big outside
terminal, it should be the same as the battery voltage. This is
illustrated in the above figure.
The Acid Test:
If you use a piece of wire to jump (temporarily connect) the small solenoid terminal to
the big outside solenoid terminal, the starter should engage the flywheel and
crank the engine. The key switch position does not matter except
the engine could start if the switch is on; so be sure the transmission is in neutral.
This is equivalent to turning the key to the start position but it
bypasses all of the logic and safety interlocks in the normal start
circuit.
Interpreting the result:
If the engine cranks normally during this test, the battery, battery
cables, and starter are OK so it's time to troubleshoot the start logic
circuits (interlocks, key switch, relay, etc.) . But if the
engine fails to crank or cranks slowly investigate the battery, cables,
and starter.

